Figures
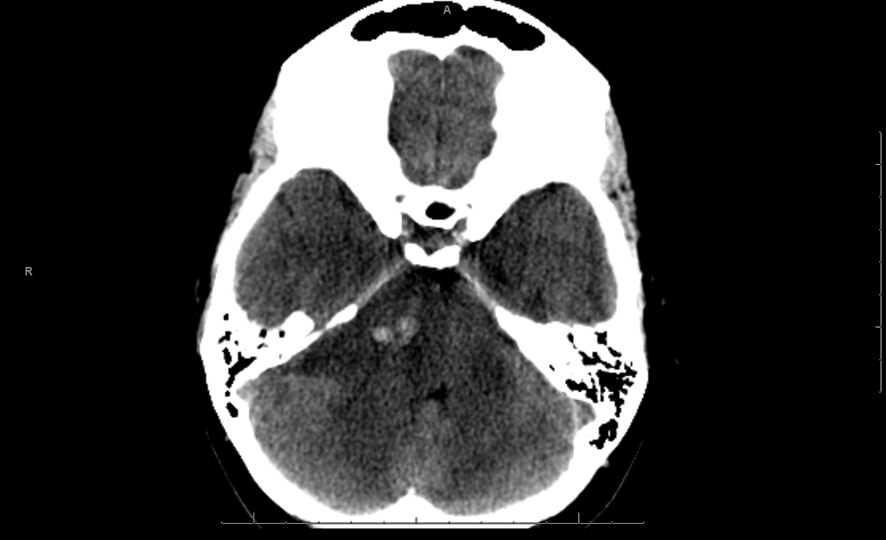
Figure 1. Single axial CT image of the posterior fossa demonstrates extra-axial mass centered on the right cerebellopontine cistern. The mass is hypodense to brain parenchyma with small central hyperdense foci of acute hemorrhage. There is moderate mass effect on the adjacent pons and ipsilateral cerebellar hemisphere.
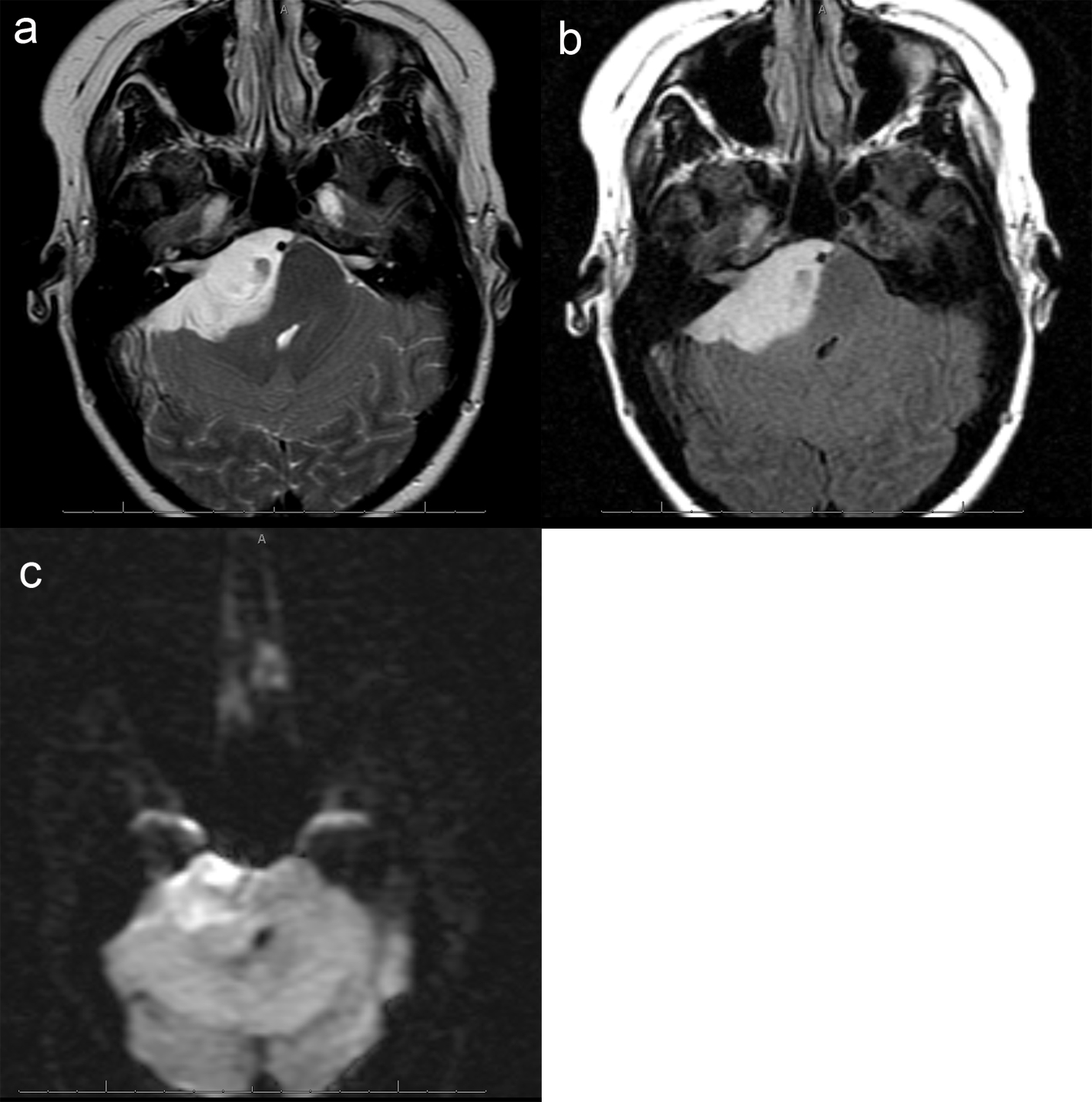
Figure 2. (a), Axial T2 image of the posterior fossa confirms the presence of a large extra-axial T2 hyperintense mass. There is mass effect on the adjacent pons and right cerebellar hemisphere. Foci of hemorrhage are present within the medial aspect of the mass. (b), Axial FLAIR image shows no surrounding edema. Focal abnormal T2/FLAIR signal is seen within the internal auditory canal of unclear significance. Abnormal signal with the same characteristics as the dominant mass extends within the right Meckel's cave. (c), Axial DWI image demonstrates mild, diffuse restricted diffusion is noted. The ADC map is not shown, however confirms the DWI findings.
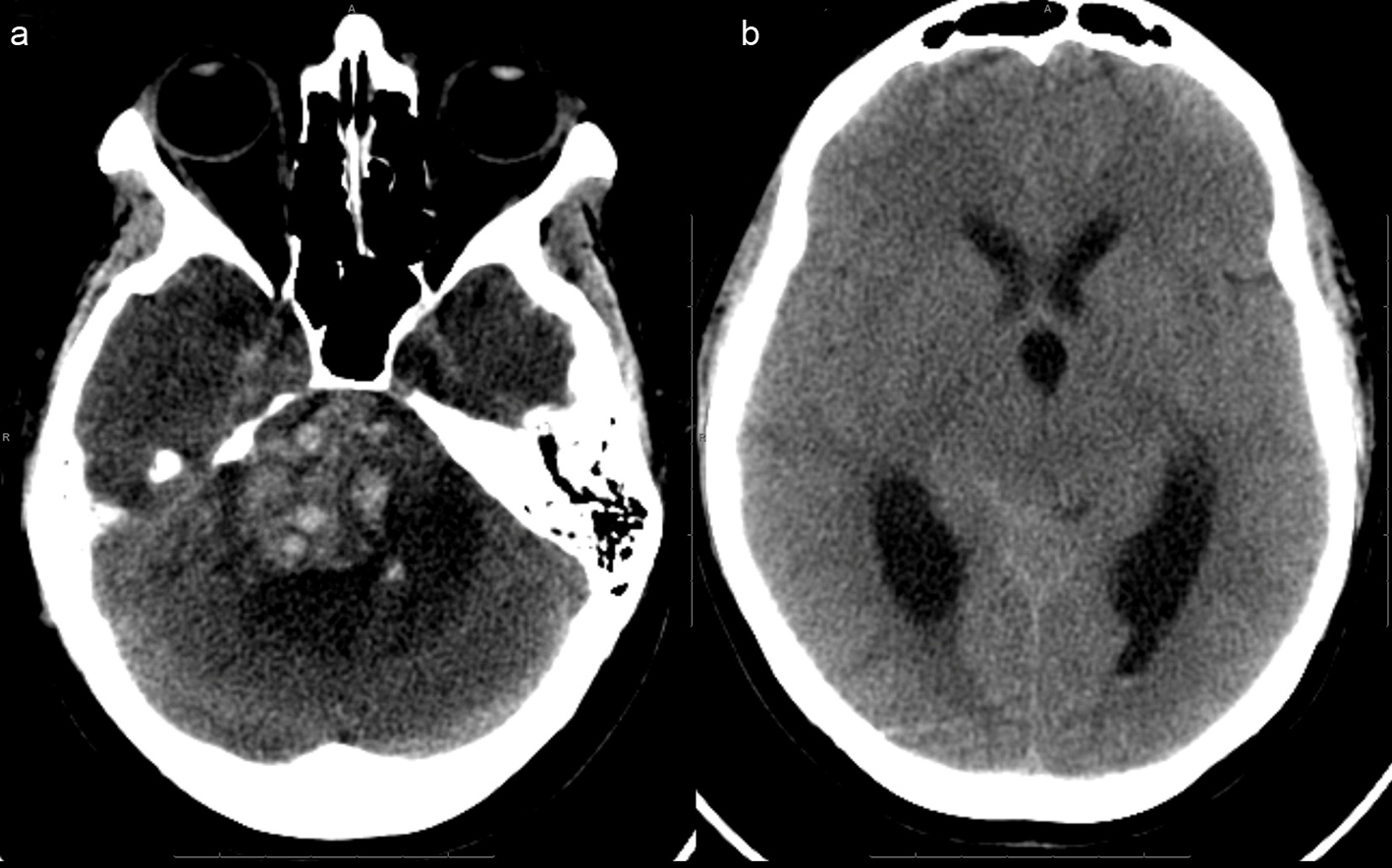
Figure 3. (a), (picture without the ventricles) Extensive acute hemorrhage is seen at the site of the right cerebellopontine cistern mass, causing mass effect within the posterior fossa, including compression of the pons and upward transtentorial herniation. There is surrounding hypodense rim, indicative of edema.(b), (picture of dilated ventricles) - Effacement of the basilar cisterns and compression of the aqueduct and fourth ventricle are noted, indicative of obstructive hydrocephalus.
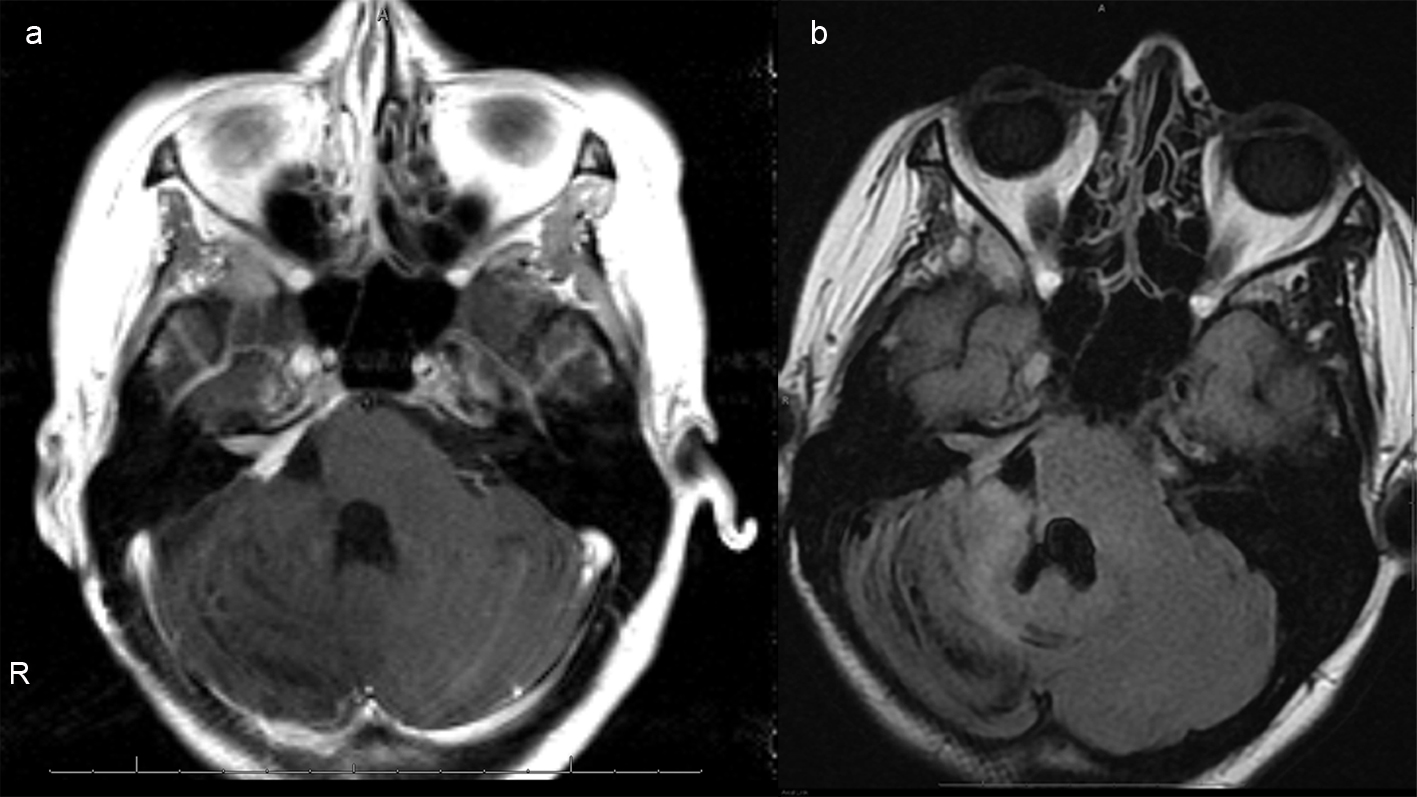
Figure 4. (a), Axial T1 postcontrast images of the brain status post gross total resection of the mass with mild residual enhancement along the right petrus ridge, internal auditory canal and Meckel's cave, indicative of residual tumor. (b), Axial FLAIR image demonstrates reexpansion of previously compressed brainstem and right cerebellar hemisphere. Susceptibility artifacts within the surgical bed indicate hemosiderin deposition. There is no hydrocephalus.
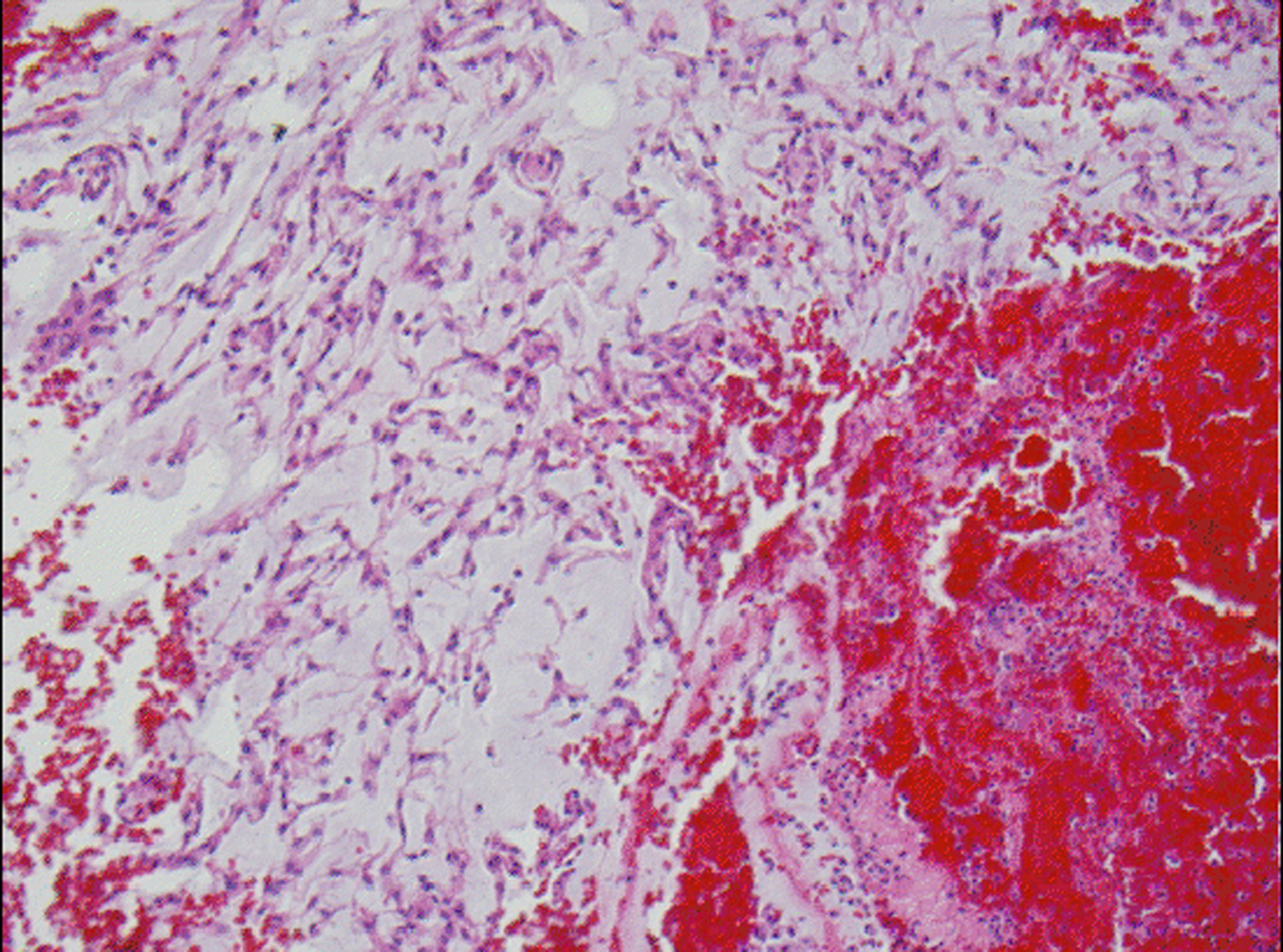
Figure 5. H&E stained slide demonstrates chordoid meningioma admixed with hemorrhage.
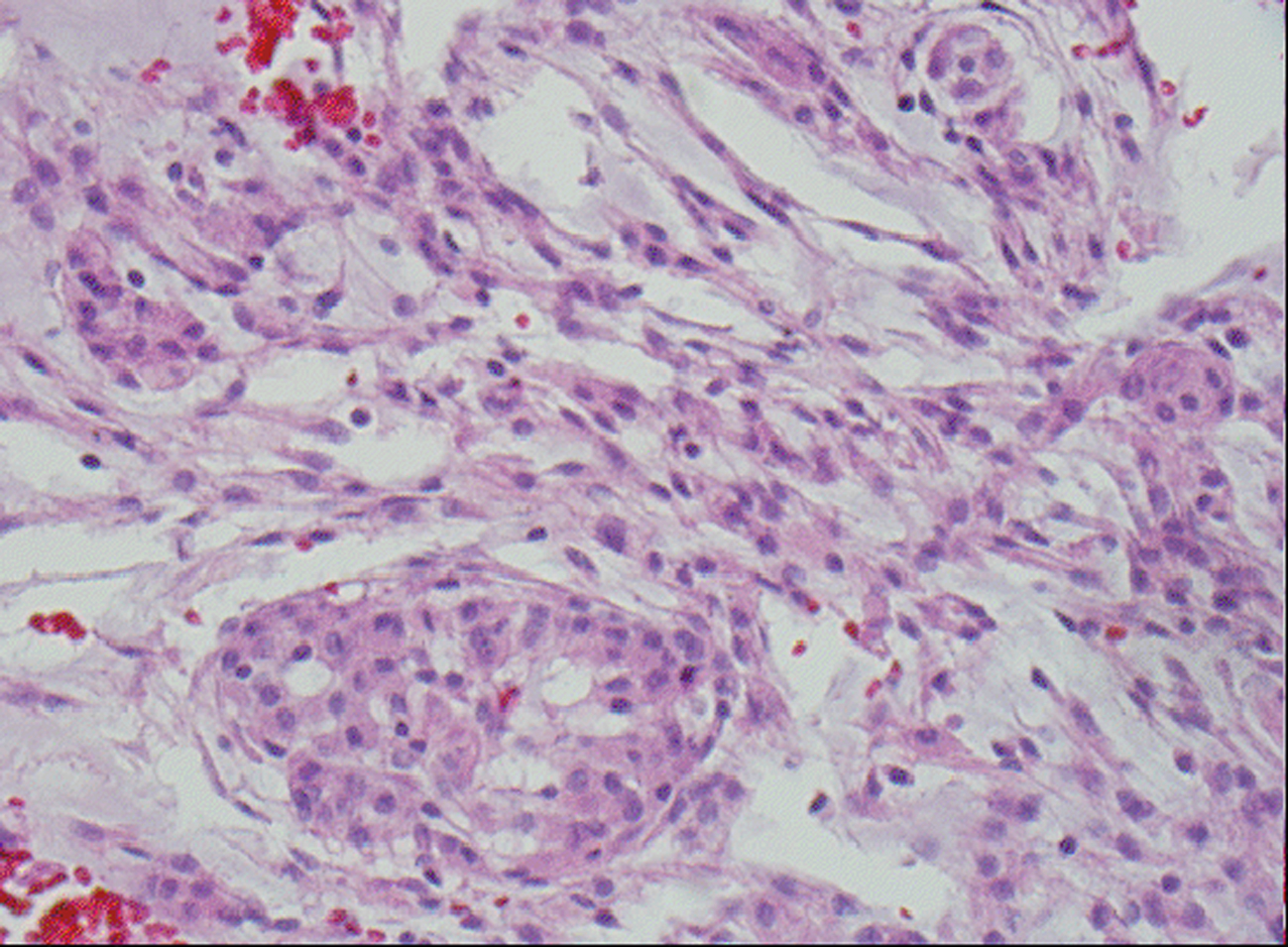
Figure 6. H&E stained slide demonstrates chordoid meningioma composed whorl formation and chordoid growth pattern with eosinophilic tumor cells in a myxoid matrix.
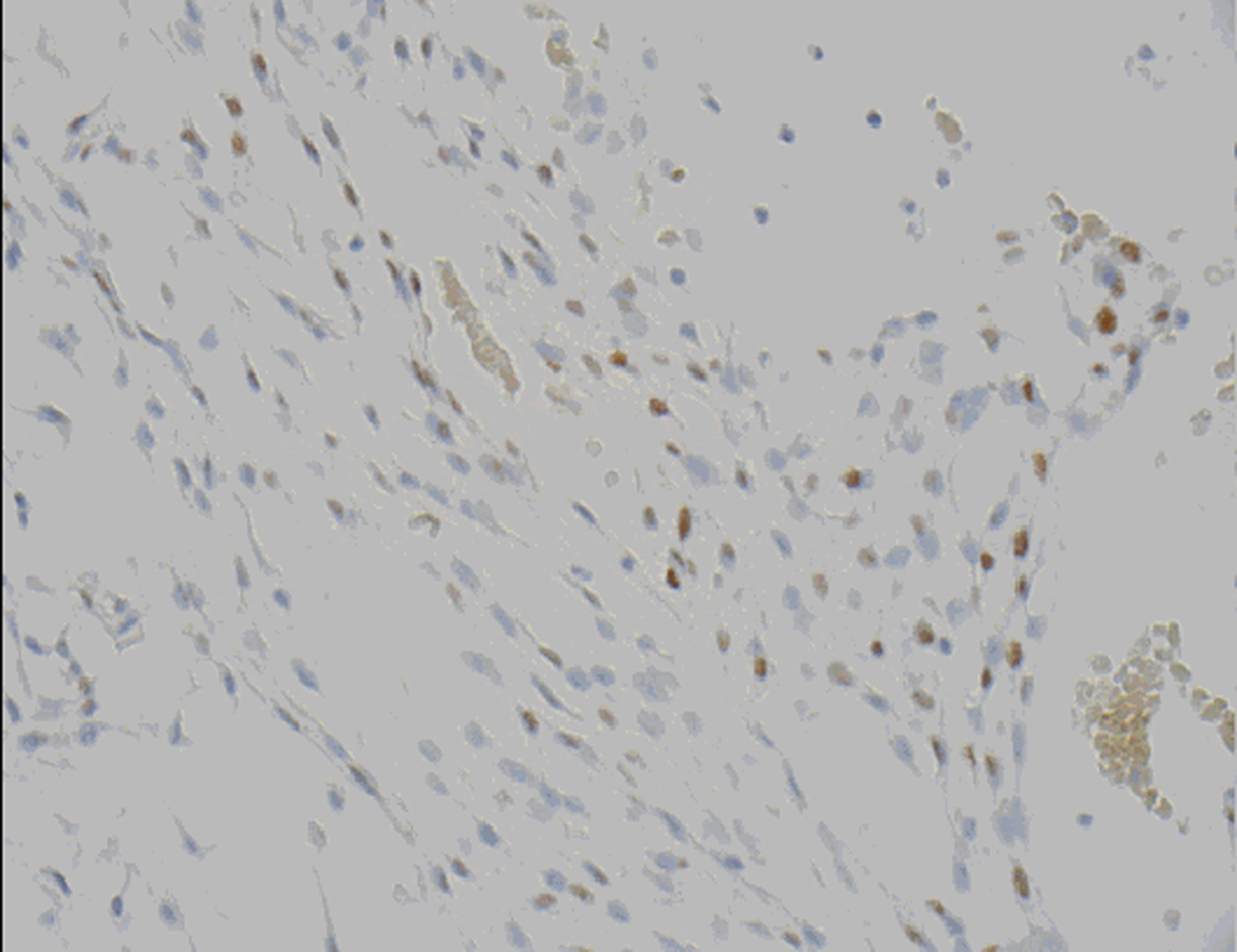
Figure 7. Progesterone receptor (PR) demonstrates nuclear positivity in chordoid meningioma tumor cells.






